Using the Database Importer (Beta)
Introduction
The databaseDatabase importerImporter allowsin theOPSCOM adminprovides administrators with a powerful tool to import their existing information into the OPSCOM system. Given a CSV file, the importer will transfer the data into the selectedsystem destinationusing table.CSV files. This functionality is essential for initial data migration, mass updates, or integrating data from external systems, ensuring that your OPSCOM database is populated and maintained efficiently. This tool is currently in BETA.
Setup & Configuration
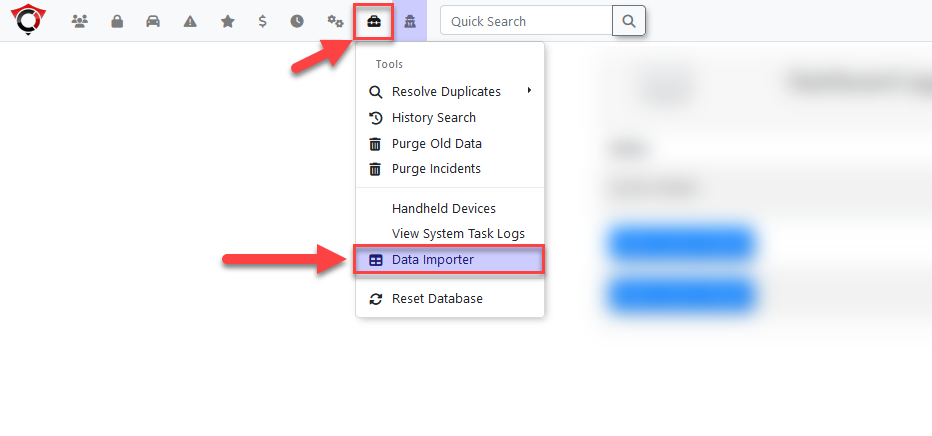
- Click Tools, Database Importer to access the tool.
Permissions Requirements
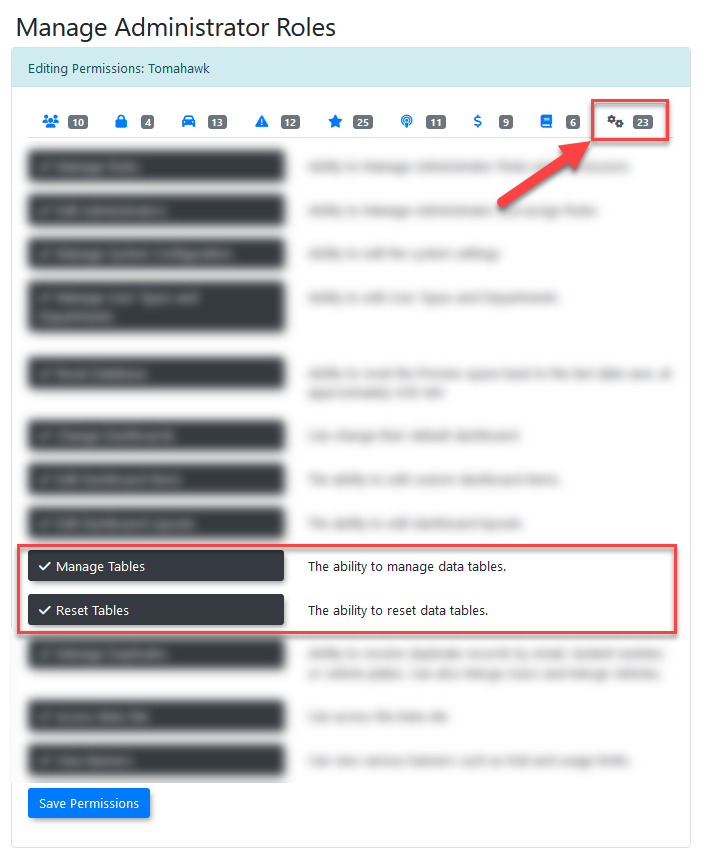
If the Database Importer page is not visible, the user's account does not have the necessary permissions enabled. To allow a user to import or manage data, the following permissions must be configured:
- Manage tables: This permission allows the user to view the Manage Tables page and utilize the upload functionality for importing data. It does NOT grant the ability to reset tables.
- Reset tables: This permission grants the ability to empty (reset) tables. It does NOT allow the user to see the Manage Tables page unless Manage tables is also enabled.
These permissions can be found under the Systems tab of the permissions management page. Enable them to grant a user access to the Database Importer functionality. For more information on configuring permissions, please refer to the User Roles and Permissions wiki article.
Using this Feature
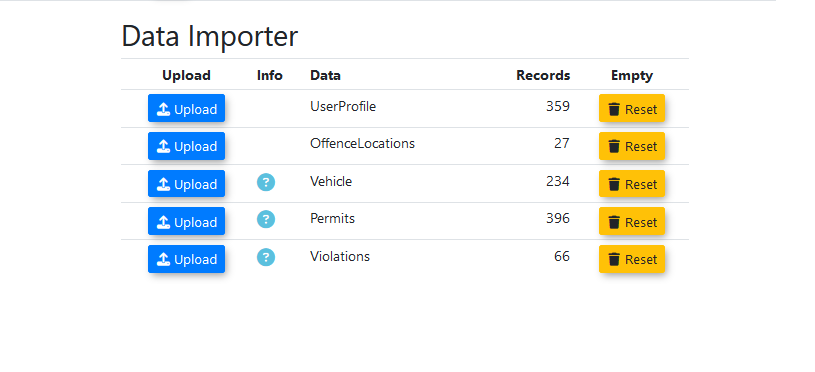
The databaseDatabase importer onlyImporter allows data to be imported into a select number of tables.tables within OPSCOM.
The
Currently currentlySupported allowedTables tablesfor are as follows:Import
UserProfile
OffenceLocations
Vehicle
Permits
Violations
Support for additional tables will continue to be added in the future.
Initial Setup
The database importer can be found listed under the tools tab.
If the database importer page is not visible, the user may not have the proper permissions. Before a user can import data, they must have the necessary permissions enabled on their account.
There are two permissions associated to table imports.
Manage tables - allows the user to view the manage tables page, and use the uploads functionality, but NOT the ability to reset tablesReset tables - allows the user to reset the tables (empty them). Won't allow them to see the manage tables page.
The permissions can be found under the systems tab of the permissions management page. Enable them to allow a user access to the page.
For more information on permissions, refer to this article: https://wiki.OPSCOM.com/x/B4DjAQ
Importing Data into a Table
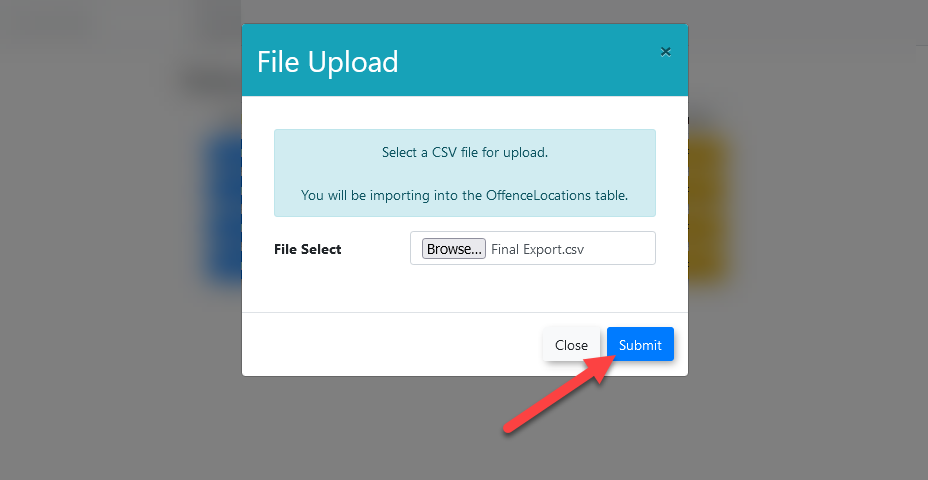
To startbegin a new import,import:
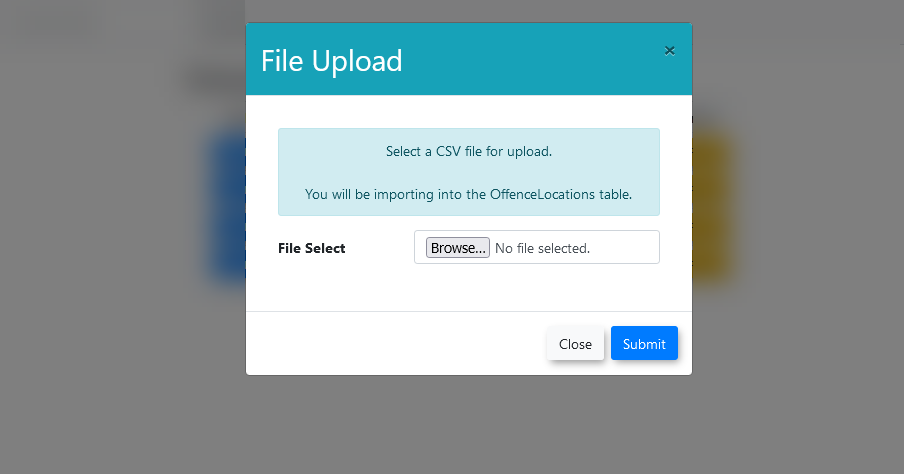
- Click the
uploadUpload button next to the desired destination tablethethat you wish to import informationwillinto. - A modal window will open, prompting
the useryou to select the CSVfilefile.they will be importing into the destination table. TheYour imported CSV file can be comma-differentiated or semi-colon-differentiated.differentiated. - Once a file has been selected,
pressclickthe submit buttonSubmit to begin the upload process. - After the CSV file has been successfully uploaded, the
tableTableimportImport screen will appear.
This will open a
Once
Converting Fields to Text to Avoid Truncating Leading Zeros - When converting data from Excel to CSV, issues can arise, such as the truncation of leading zeros in numbers (e.g., student IDs, staff numbers). To prevent this, you can force Excel to treat cells as text before converting to CSV as below:
- Open a
Excel workbook.
="'"& then click on cell A1 of your original spreadsheet. (This formula is: equals sign, double quote, apostrophe, double quote, ampersand, then the cell reference.)') will be placed in front of all values, forcing Excel to treat them as text..CSV file. Ensure you only save the new page. This method effectively preserves leading zeros during the CSV conversion.Column Matching
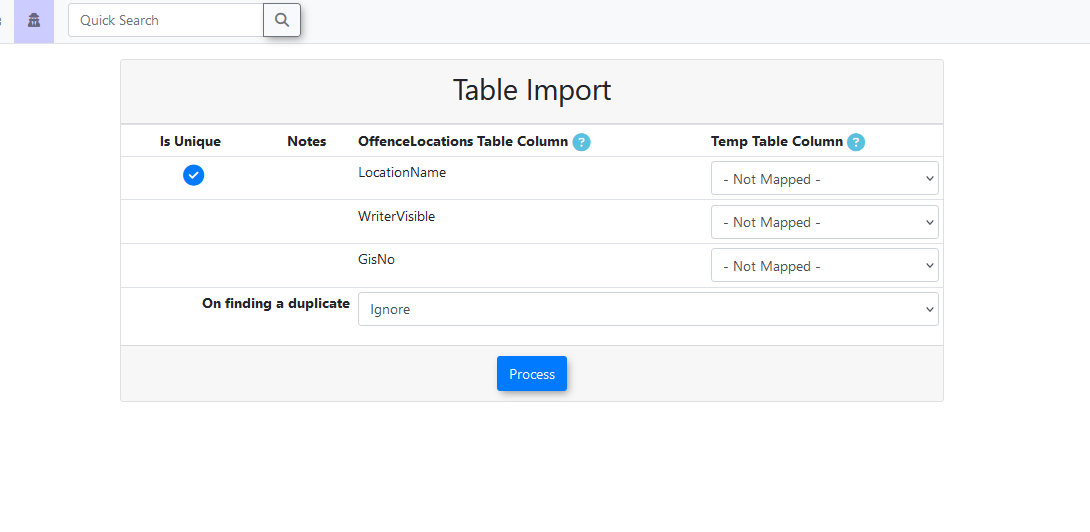
On thisthe page,Table Import screen, you will match the columns from your imported CSV file to the corresponding columns in the imported file are matched to the columns existing in the destination table.table within OPSCOM.
- This
isstepto letinforms the programknowwheretheeach piece of data fromtheyour CSV file belongs in the destination table. - If
theyour CSV file contained recognized column names,theythe system willbeautomaticallyselected.pre-selectthe appropriate matches.
- For
moredetailed information onwhateachcolumncolumn'sis used for, orpurpose, whethera columnit is required or optional, and specific formatting, please refer tothisthe Importer Field Descriptions guide.
OneOnce the columns have been properly matched and theyou process button has been pressed,click the userProcess button, you will be redirected back to the main page while the import is completed in the background.
If an email address is setup on the importing user's account, they will be informed on the progress of the import by emails sent to their email address.
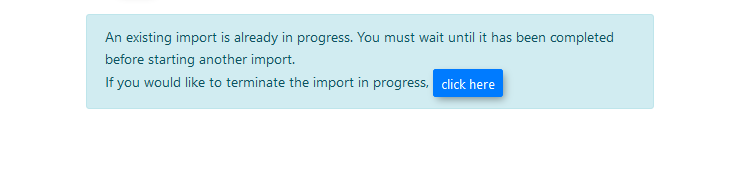
Another import cannot be started until the current one is either completed or has been terminated. Terminating the progressing import will delete the temp tables created during the import, and isn’t recommended unless the import has become stuck.
Post-Import Processing
and Settings
After the initial import of the data into the base table, some tables run additional processing on the information.
to establish relationships and apply default settings. These processes run separately from the initial import process, and are not affected by the duplicate settings chosen for the import.
After this process has been completed, the user will be sent a second email containing the final details of the import, including how many records were imported, updated, and any post-processing details.
Permits
If the user association column is matched, the created permit will have a booking automatically created for the associated user through the creation of a PermitJoin record.If the option was selected, the newly-created permits that were booked to users will be automatically marked as paid. Otherwise, they will be located in the users' carts and the users must pay for them.
UserProfile
When users are imported, if they aren't provided a LoginSource, it will be automatically set to OPSCOM.Users that are created are set to enabled automatically.
Vehicle
If the user association column is matched, the created vehicle will be automatically associated to the user through the creation of a VehicleJoin record.If the alert column is matched, an alert will be created and automatically attached to the associated vehicle through the creation of an AlertComments records. The vehicle will also be flagged.
Violations
Any violations created that don’t have an Issued date and Due date will have one created for them at the time of the import.
OffenseLocations
This table has no post-processing.
Additional Settings
Additional details on import settings.
Order of Operations
Imports that contain related information have a general order they should be done in, as some of the tables contain information from another table.
The imports are able to be done out of order, but the records cannot be associated correctly to each other when done out of order.
In general, the imports the table requires should be imported before it is.
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
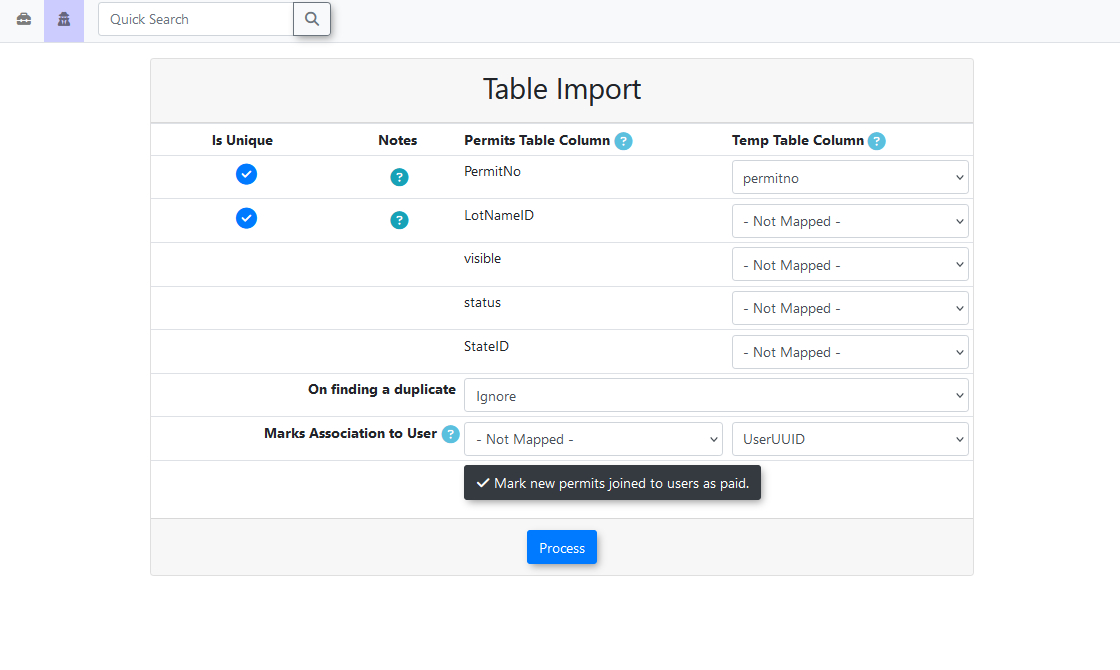
User-Association Settings
Some tables have additional processing that is run after the import is completed to associate the newly-created records to existing users.
For this, the record identifying the uniqueness of the user must be selected.
It can either be UserUUID or Email, so make sure the same value is selected for both sections.
The tables that currently have this as an option are:
VehiclesPermits
Mark Permits as Paid
Permit importing has an additional option for if you would like to have the booked permits that are created automatically marked as paid.
Otherwise, when they are created, they will be located in the associated users' carts.
Vehicle Alerts
Vehicle importing has an additional option for setting up an alert on a vehicle automatically when they are created.
Include a column containing vehicle alert comments within the imported CSV file and select the column in the alert section of the vehicle import page.
Alerts will be automatically associated to the proper vehicle after import.
The list of vehicles being marked with alerts may also be called a hotlist.
Unique Identifiers & Duplicate Settings
This is the column that is used to tell if the information in the record is unique. If the information in this column is duplicated in the file or already exists in the system, it will be ignored or overwritten based on the selected setting.
Ignoring a duplicate will have the system do nothing with the record.Overwrite existing will take the information in the new record and replace the existing record with it.
The number of columns that mark a record as unique varies from table to table.
UserProfileuses one identifier, which can either be UserUUID or Email. For this table, it is one or the other, with UserUUID taking precedence over Email if both columns are supplied.OffenceLocationsuses one identifier, which is LocationName.Vehicleuses one identifier, which is Plate.Permitsuses two primary identifiers, PermitNo and LotNameID. Both are required to make a unique record, meaning identical PermitNo can be in use if they have different LotNameIDs.Violationsuses one identifier, which is Ticket.
Foreign Lookup Columns
Some information in one table comes from another table and is stored as an ID in the destination table.
The data in these columns should be entered as normal, then the system will automatically look to see if there is a match in the corresponding table and input the correct ID value into the destination table.
For instance, one of the foreign keys for the Vehicle table is Colour, stored in the VehicleColour table. If any of the values in the column imported for Colour exist in the VehicleColour table, it will match them by name and store the proper ID in the Vehicle table.
If it doesn't find a matching value in the lookup table, it will enter a Null as the value instead.
A list of the import tables are listed below.
UserProfile Table
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Vehicle Table
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Permits Table
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Violations Table
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Status Emails
Over the course of the import process, a total of two emails will be sent to the user who initiated the import:
The first email is sent after the data from the CSV has been inserted into the
temptemporarytable,table.andIt records the number of rows that weresuccessful,successfully imported and the rows that failed due tobe imported because they werebeing malformed.The second email is sent after the data has been inserted into the base
occurred.table.table and post-processing is complete. It contains the number of records that wereupdated in the base table,updated, the number of recordsinserted into the base table,inserted, and any relevant information from the post-import processing thathappened.
Table-Specific Post-Processing Details
- Permits:
- If the user association column is matched, the created permit will automatically have a booking created for the associated user via a
PermitJoinrecord. - If the option was selected during import, newly-created permits booked to users will be automatically marked as paid. Otherwise, they will be located in the users' carts, requiring users to complete payment.
- If the user association column is matched, the created permit will automatically have a booking created for the associated user via a
- UserProfile:
- When users are imported, if a
LoginSourceis not provided, it will be automatically set to OPSCOM. - Newly created users are automatically set to enabled.
- When users are imported, if a
- Vehicle:
- If the user association column is matched, the created vehicle will be automatically associated with the user via a
VehicleJoinrecord. - If the alert column is matched, an alert will be created and automatically attached to the associated vehicle via an
AlertCommentsrecord. The vehicle will also be flagged. The list of vehicles being marked with alerts may also be called a hotlist.
- If the user association column is matched, the created vehicle will be automatically associated with the user via a
- Violations:
- Any violations created that do not have an
Issued DateandDue Datewill have one automatically generated for them at the time of import.
- Any violations created that do not have an
- OffenceLocations:
- This table has no specific post-processing.
Order of Operations for Related Imports
Imports that contain related information should generally be done in a specific order, as some tables contain information that references another table. While imports can be done out of order, records may not be associated correctly if their dependencies aren't met. In general, the tables a record requires should be imported before that record's table.
User-Association Settings
Some tables include additional post-processing to associate newly-created records with existing users. For this to work, the unique identifier for the user (UserUUID or Email) must be selected consistently for both the user's primary record and any associated records (Vehicles, Permits). Ensure the same value is selected for both sections during the import setup.
The tables that currently have this user-association option are:
- Vehicles
- Permits
Unique Identifiers & Duplicate Settings
The Unique Identifiers are the columns used to determine if a record's information is unique. If the information in these columns is duplicated in the file or already exists in the system, it will be handled based on your selected Duplicate Settings:
- Ignoring a duplicate: The system will do nothing with the duplicate record.
- Overwrite existing: The information in the new record will replace the existing record with the same unique identifier.
The number of columns that mark a record as unique varies by table:
- UserProfile: Uses one identifier, which can be either UserUUID or Email. If both are supplied, UserUUID takes precedence.
- OffenceLocations: Uses one identifier, which is LocationName.
- Vehicle: Uses one identifier, which is Plate.
- Permits: Uses two primary identifiers: PermitNo and LotNameID. Both are required to make a unique record, meaning identical
PermitNovalues can exist if they have differentLotNameIDvalues. - Violations: Uses one identifier, which is Ticket.
Foreign Lookup Columns
Some data in one table originates from another table and is stored as an ID in the destination table (known as a foreign key).
- Data in these columns should be entered as normal text in your CSV. The system will automatically look for a match in the corresponding lookup table.
- If a matching value is found (e.g., a "Colour" name in the
VehicleColourtable), the system will input the correct ID value into the destination table. - If no matching value is found in the lookup table, the system will enter a
Nullvalue instead.
Below is a list of common foreign lookup columns and their source tables:
Table Reset
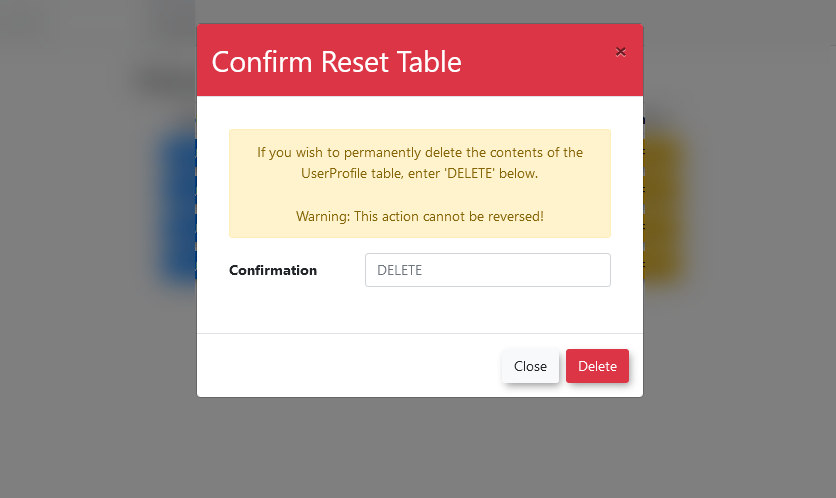
In addition to tableimporting imports,data, the Database Importer page also allows for the purging of aan table.entire table's contents.
-
Click
onthe Reset buttonthat says Resetnext to the table you wish tobe emptied.empty. -
This will open aA new modalwindow,window will open, promptingthe useryou to confirmtheythat you wish to delete the contents of the table.<callout type="warning" title="Irreversible Action"> This action is
permanent,permanent.and onceOnce the data is deleted, it cannot be recovered. Ensure you are absolutely certain before proceeding. </callout> -
If
ityouisare certain the data should be deleted,entertype DELETE (in all caps) into the confirmation text field and press thedeleteDelete button. -
The selected table will then be purged of all records.
Related Table Purges
Some tables are closely connected to the records of a related table,table. and removingRemoving the data they contain will also purge the contents of the related table.table:
Purging the Vehicle table will also purge the VehicleJoin table.
Purging the Permits table will also purge the PermitJoin table.
NoteNote: that onlyOnly the table contents are deleted, anddeleted; the table structure itself remains intact.
TroubleshootingBest Practices & Considerations
Converting
Fields-
Data Preparation is Key: Ensure your CSV file is meticulously prepared. Accurate data, correct formatting, and adherence to Textspecified -column Avoidnames Truncating(if Leadingknown) Zeros
will significantly reduce import errors.
Data Preparation is Key: Ensure your CSV file is meticulously prepared. Accurate data, correct formatting, and adherence to Textspecified -column Avoidnames Truncating(if Leadingknown) Zeros
InBackup someBefore cases,Import: theWhile conversionnot fromexplicitly Excela system feature, it's a best practice to .CSV, will create some issues by truncating the leading zeros on your Student or Staff numbers for example. If this happens, you can use the following format to tell Excel to convert your cells to Text so that this information survives the .CSV conversion.
An example of how you do this is below.
Open a new sheet on the spreadsheet you wish to convert to text.In cell A1, type ="'"& then click on cell A1 on the original spreadsheet. Note, this is equals sign, double quote, apostrophe, double quote,Now drag this formula down through the same amount of rows and columnsensure you haveonrecent system backups before performing large-scale imports or table resets.-
Understand Dependencies: Always review the
first"Ordersheet.ofThisOperations"willbeforereplicateimporting, especially when dealing with related tables like UserProfile, Vehicles, and Permits. Importing out of order can lead to unassociated records. -
Handle Duplicates Strategically: Choose your "Duplicate Settings" (Ignore or Overwrite) carefully based on whether you intend to add new unique records or update existing ones.
-
Monitor Status Emails: Pay close attention to the
datastatus emails sent during the import process. They provide crucial feedback onthesuccessnew page but the apostrophe will be in front of all values.. Now save the file as a .CSVrates andonlypotentialtheissues.newpagewill save.No more truncated leading zeros.