IP Filtering for Admin Users
IP Filtering in OPSCOM provides administrators with a robust security layer by restricting user access based on their device's IP (Internet Protocol) address. This feature enhances system security by ensuring that only authorized users from specified networks or devices can log in to OPSCOM, allowing for tailored access control according to individual roles and organizational security policies.
Setup & Configuration
IP filtering configurations are managed within each administrator's user profile in OPSCOM.
What is an IP Address?
An IP address is a unique numerical label assigned to each device connected to an IP network. It typically consists of four groups of numbers (octets), separated by dots (e.g., 192.168.1.1).
- The first two octets generally identify the network your device is on.
- The last two octets further narrow the address down to a specific machine within that network.
- To find your current public IP address, you can visit a website like
whatismyip.netor simply search "What is My IP" in Google.
To Configure IP Filtering in OPSCOM:
- Hover over the System Configuration, then Admin Management, and click Edit Admin Users.
- On the Manage Active Administrators page, select the specific user you wish to edit.
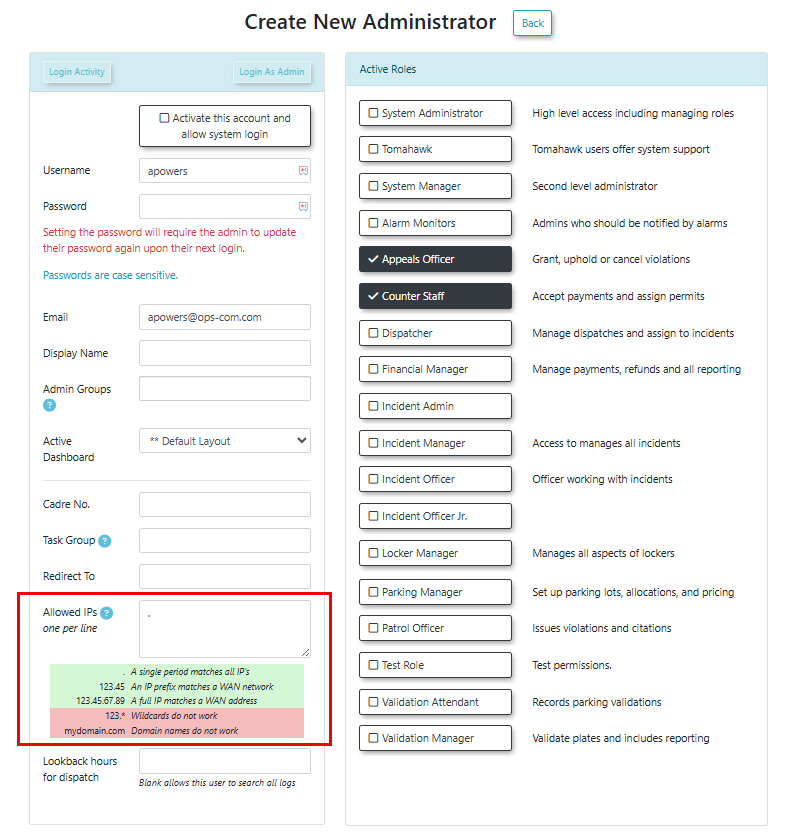
- Locate the Allowed IPs field within the user's profile configuration. This is where you will enter the IP filtering rules.
Using this Feature
The Allowed IPs field in an admin user's profile controls their access to the OPSCOM system. The level of access can be precisely tailored:
Configuration Options for Allowed IP Addresses
Allow Access from Any Network (Least Restrictive)
This is typically used for high-level managers or directors who require access from diverse locations (e.g., while traveling, from a home office, or an internet cafe).
Note: In some cases, networks might be locked down or behind a firewall. Additional configuration on the part of your IT department may be required to allow external access.
- Configuration: Enter a single dot (
.) in the Allowed IP Addresses field. - Result: The user will be able to log in from literally any network location, whether internal or external to your organization's specific network.
Restrict Access to a Specific Network
This is ideal for regular office workers who primarily require access only from their designated office network.
- Configuration: Enter the first two octets of the network's IP address (e.g.,
10.32). - Result: The user can log in from any computer connected to that specific network, but will be restricted from accessing OPSCOM from any other network.
Restrict Access to a Specific Computer (Most Restrictive)
This is suitable for part-time employees or student workers who are designated to use only one particular machine for OPSCOM access.
-
- Configuration: Enter the full IP address of the specific computer (e.g.,
10.32.1.144). - Result: The user can only log in to OPSCOM from that single, specified computer.
- Configuration: Enter the full IP address of the specific computer (e.g.,
Allow Access from Multiple Specific Computers
This is useful in office settings where an employee may use a few designated workstations.
-
- Configuration: Enter the full IP address of each allowed computer, placing each address on a separate line within the Allowed IPs field (e.g.,
10.32.1.144followed by10.32.1.154on the next line). - Result: The user can log in from any of the explicitly listed computers.
- Configuration: Enter the full IP address of each allowed computer, placing each address on a separate line within the Allowed IPs field (e.g.,
Allow Access from Multiple Specific Networks
This is applicable for employees working out of multiple campus locations or different buildings within a municipal organization, each on a distinct local area network.
-
- Configuration: Enter the first two octets of each allowed network, placing each network segment on a separate line within the Allowed IPs field (e.g.,
10.32on one line and10.40on another). - Result: The user can log in from any computer on the specified networks.
- Configuration: Enter the first two octets of each allowed network, placing each network segment on a separate line within the Allowed IPs field (e.g.,
Basic IP Filtering Rules Recap
-
Good Configurations:
.- A single period to match all IP addresses (least restrictive).10.32- A partial IP address to match all computers on a specific network.10.32.1.144- A full IP address to match a specific computer (most restrictive).
-
Invalid Configurations:
10.*- Wildcards (*) like this will not work.OPSCOM.com- Domain names will not work; only numerical IP addresses are supported for filtering.
Best Practices & Considerations
- Security vs. Flexibility: Balance the need for security with the practical access requirements of your administrators. More restrictive settings (full IP) offer higher security but less flexibility.
- Dynamic IPs: Be aware that many internet service providers assign dynamic IP addresses that can change over time. If your administrators access OPSCOM from external locations with dynamic IPs, using a full IP filter will frequently require updates, making the "single dot" setting often more practical for such scenarios.
- Internal Network Changes: If your organization's internal network IP scheme changes, remember to update the Allowed IPs field for all affected administrators.
- IPv6 Consideration: When using IP filtering, it is generally recommended to enter your IPv6 IP address if your network primarily uses IPv6, as IPv4 addresses are becoming less common for external facing services.
- IT Department Collaboration: For complex network setups, especially involving firewalls or VPNs, collaborate with your IT department to ensure proper network configuration aligns with your OPSCOM IP filtering rules.